Beneath the Pulse: Hidden Patterns of Resistant Hypertension and Renal Microvascular Damage in Treated Patients
Matteo Romano¹ , Elisa Conti² , Leon Zimmermann³
Keywords:
Resistant Hypertension, Renal Microvascular Damage, Doppler Ultrasound, Internal Medicine, Kidney FunctionAbstract
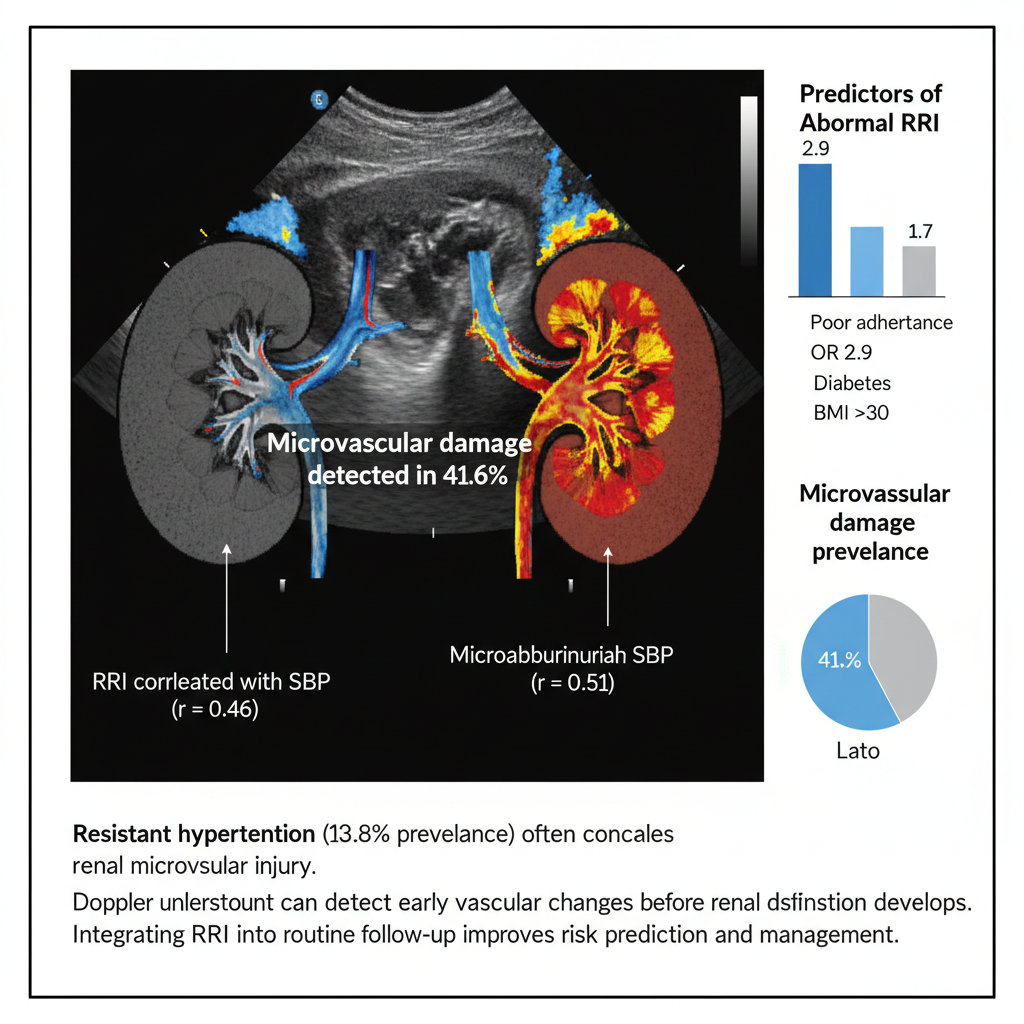
Background: Resistant hypertension (RH) persists in 10–15% of treated hypertensive adults and is linked to subclinical kidney injury. Microvascular changes often precede overt dysfunction.
Objective: To determine the prevalence of renal microvascular damage among RH patients and evaluate associated predictors.
Methods: In this multicenter cross-sectional study (n = 842, mean age = 56 ± 9 years), hypertensive adults on ≥3 medications were enrolled. Renal Doppler resistive index (RRI) and microalbuminuria were measured. Logistic regression identified predictors of abnormal RRI (>0.7).
Results: RH prevalence = 13.8%. Microvascular damage was detected in 41.6% (95% CI 37.9–45.2). Independent predictors were poor medication adherence (OR 2.9, p < 0.001), diabetes (OR 2.1, p = 0.01), and BMI > 30 kg/m² (OR 1.7, p = 0.04). Mean RRI correlated with systolic BP (r = 0.46, p < 0.001) and microalbuminuria (r = 0.51).
Conclusion: Subclinical renal damage affects 4 in 10 patients with resistant hypertension. Routine Doppler evaluation should complement blood-pressure control strategies to prevent end-organ failure.
Downloads