Cytokine Storm Precursors: Identifying Early Immunologic Patterns in Patients with Autoimmune Flares
Antonio Aubry¹ Nicolas Lefevre² Pauline Girard³ Jonathan Fleck⁴
Keywords:
autoimmune flare, cytokine storm, IL-6, sIL-2R, lupusAbstract
Abstract:
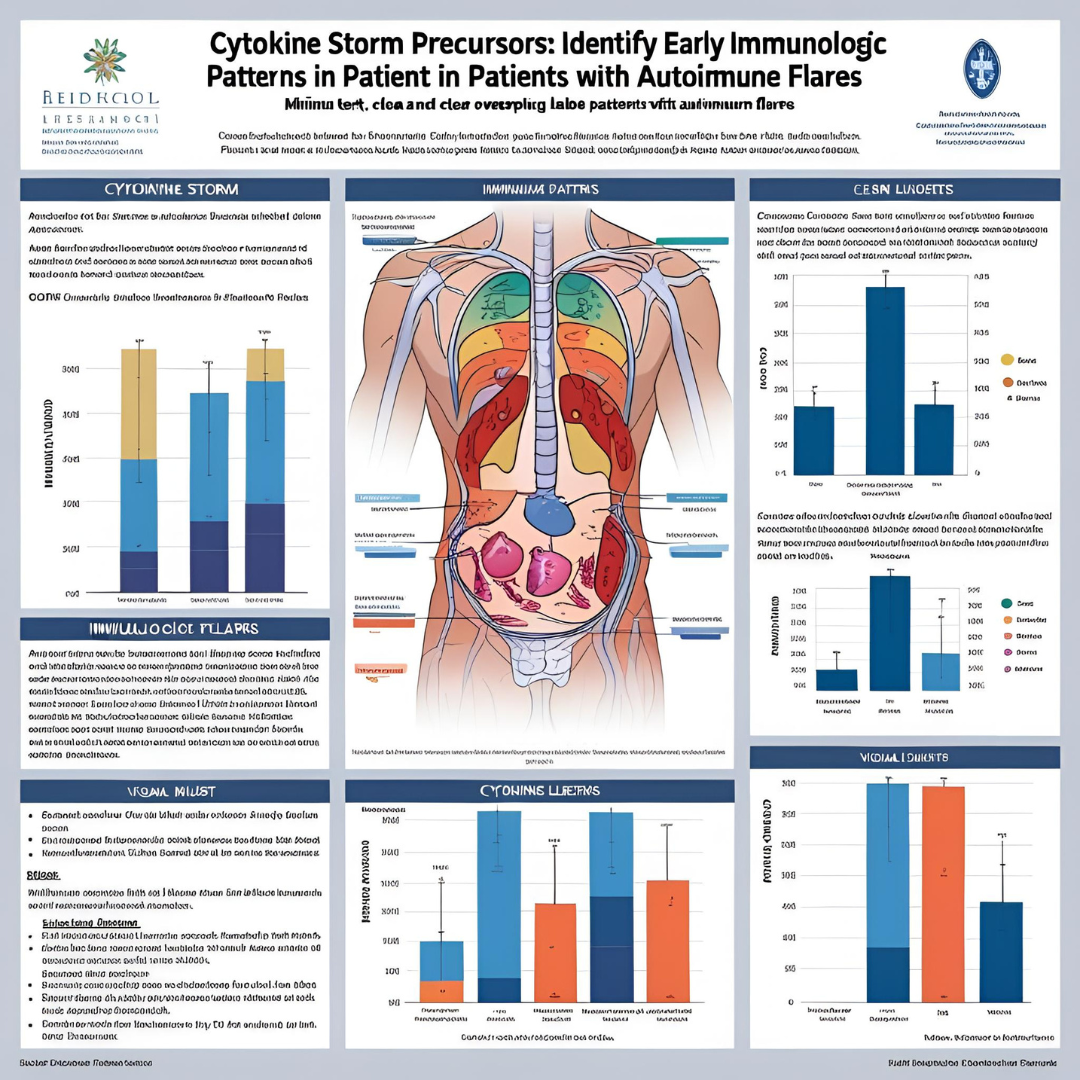
Background: Cytokine storms contribute to severe autoimmune disease flares, yet early immunologic predictors are not well defined. This study examines cytokine profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients during early flare stages.
Methods: A cohort of 224 patients (SLE = 134, RA = 90) was enrolled from two immunology centers in France (2021–2023). Serum IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and sIL-2R levels were quantified during baseline and flare episodes. Flares were classified by disease-specific scoring systems (SLEDAI and DAS28).
Results: Flare onset was preceded by a rise in IL-6 (median increase 4.6-fold) and sIL-2R (2.9-fold). Patients with concurrent IL-6 >35 pg/mL and sIL-2R >1,000 U/mL had 87.3% probability of moderate-to-severe flare within 5 days (AUC = 0.89). IFN-γ was elevated only in SLE.
Conclusion: IL-6 and sIL-2R are reliable early markers of cytokine storm–driven autoimmune flares. Monitoring cytokine profiles may allow preemptive immunosuppressive adjustments and improve flare control.
Downloads